ANALYSIS OF PALLET RACK TYPES
Selective Pallet Rack
Selective pallet racking is the most common type of pallet storage used today. Selective rack uses uprights and a pair of cross beams to create a “shelf” for storing a pallet. Depending on the height of your pallet and ceiling, selective rack systems typically have multiple levels (shelves) per bay. A bay is typically only one pallet deep, although two-deep systems are also a possibility.
Advantages:
- Low investment compared to more dense storage solutions
- Accessibility to all pallets
- FIFO or LIFO
- High throughput volume and accessibility
- Good for if you use forklifts around your warehouse frequently.
Disadvantages:
- Low storage density
- Limited by one-two pallets deep
Drive-In and Drive-Through Pallet Rack
Drive-in racking is a type of storage system that allows fork trucks to drive directly into a bay. Pallets rest on side rails rather than cross beams, which leaves the face of the bay open. The uprights are typically tied together at the top of the upright to add rigidity to the system. The only difference between drive-in and drive-through racks is whether there is an entrance at only one end (drive-in) or both ends (drive-through).
This style of rack is commonly 6-8 pallets deep per bay. Fork trucks elevate a load to the proper level and load it in the back of the system first. The second pallet will be placed in the second position from the back and continue until a lane is full. Drive-in racks are LIFO, while drive-through racks are typically FIFO. This type of system is best suited for storing a large quantity of pallets of the same product.
Advantages:
- High storage density
- Lower cost than a flow rack system
Disadvantages:
- Poor accessibility to all pallets
- Rack often gets damaged since fork trucks drive inside the system
Pallet Flow Rack System
This type of racking uses uprights and cross beams to support a gravity roller conveyor within the rack. The rollers are pitched slightly, so pallets will naturally flow toward the front of the system. When a pallet is unloaded from the front of the system, the next pallet in line moves forward to the exit position. Like drive-in racks, this type of system is best suited for storing a large quantity of pallets of the same product. Pallet flow rack systems are FIFO.
Advantages:
- High storage density
- Can be stored 20+ pallets deep
- No need to drive inside the racking system
Disadvantages:
- Poor accessibility to all pallets
- Highest investment when compared to the other storage options
Push Back Pallet Rack
Push back racks are like flow rack, except the pallets are loaded and unloaded from the front of the system. The pallets can rest on either nested carts or gravity rollers. Pallets are loaded into the system by placing the inbound pallet against the pallet in the exit position and pushing it back into the lane.
Advantages:
- High storage density
- Only one aisle is needed for loading/unloading
Disadvantages:
- Poor accessibility to all pallets
- Can only be stored 4-5 lanes deep
If you find yourself in need of additional floor space, I hope these pallet storage options give you some guidance, but don’t hesitate to consult a local pallet rack distributor. They can also help you determine what style of racking best fits your needs.
Double Deep Pallet Rack
This is an extremely dense storage system that consists of two rows of pallets back-to-back, hence the term “double deep.” The concept is quite like the selective pallet rack, but instead of just two back-to-back rows, there is now a total of four. Despite its density, you’re still able to access the pallet from both sides. You can increase your floor space between 60 and 65 percent by using the double deep pallet rack because you reduce the number of aisles you need. This is a cheaper alternative to the drive-in rack.
FILO
Advantages:
• Increases storage density
- Maximizes warehouse space
- Offers the same density as a two-deep pushback pallet rack system at a fraction of the cost.Disadvantages:• Must have a forklift specifically made for the double deep system.
Pallet Racking Design
- Definitions – An upright frame (1) is constructed of two vertical columns with bracing (2) between them. Horizontal beams (3) connect the uprights together and support the pallets.
- Rack Profiles – A “profile” is a drawing that shows the distance between beam levels for each bay of rack. If there are long spans between beam levels, additional bracing may be required.
- Reinforcement – Additional bracing of the upright frame may be required and is determined by the distance between beam levels and the seismic classification. This can include bracing that is thicker, bracing that has been doubled, and a different bracing pattern that is closer together.
- Beam Design – Beam design is driven by the seismic classification which determines the size and type of connector and how the connectors are welded to the ends of the beams. The length of the beams is determined by establishing the clearances required between pallets as they are stored on the rack as well as the distance required between the pallets and the rack uprights. Typical clearances normally fall within 4” to 6”.
- Closed Tube or Open Tube – This refers to the construction of the vertical columns of the upright frames. Columns can have an open back (“open tube”) or closed back (“closed tube”). Many times, the choice is customer preference, but there can be advantages of one over the other depending on the application.
- Structural Steel Racking – Structural steel may be utilized in lieu of formed steel racking, based on the application. Traditionally structural steel racking is more expensive than formed steel racking but can also provide increased load capacities if needed.
- Column Punching – the holes that are punched in the face of the vertical columns to which the beams are connected vary greatly by manufacturer. This is important in case the punching needs to match existing pallet rack.
- Pallet Racking Accessories – The most common accessories are wire decks, pallet support bars, column protectors, and end-of-aisle guarding. Please let your integrator know if these are required or desired for the application.
- Pick-Up and Drop-Off Stations – Pallet racking is typically designed with one bay removed from the end of every other row, so pallets can be temporarily stored on the floor until they can be put away inside the racks. These are referred to as P&D Stations (Pick-Up and Drop-Off Stations).
Pallet Racks Types
High Density, Inc. Pallet Rack Systems are constructed for seismic applications and are designed to maximize storage capacity and space utilization. Several styles of Pallet Rack are available. Enhanced workflow impacts the “best” storage solution.
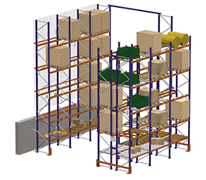
Conventional Pallet Rack is the most widely used form of pallet storage. This rack utilizes overhead space in order to safely store pallets of product vertically. This type is an excellent solution for warehouses that need to store palletized products with a side range of s.k.u.
In order to store a large number of pallets, double-depth racks can be installed enabling one pallet to be placed in front of another on each side of the aisle.
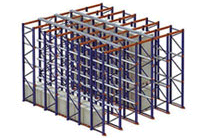
Drive-In Pallet Racking offers the highest use of available space in terms of both area and height. Pallets are set in place along a rail system at each pallet level by a forklift. The pallets must be loaded and unloaded in a specific manner, top to bottom, back to front, for the system to be effective.
The key advantage of Drive-In Pallet Racking is maximum use of available space (85%) by the elimination of aisles between the racking.
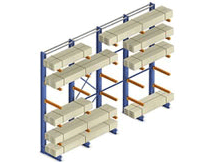
Cantilever Rack Systems are the most cost effective use of space for: lumber, pipe, and furniture. It is efficient for storage when the product is longer than a pallet. It also allows cumbersome products to be stacked where floor stack is impossible, or the product must be readily accessible.
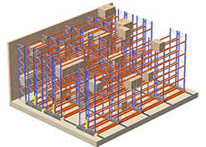
Mobile Pallet Racking is a space saving solution where the racking is installed on mobile carriages with the result of reducing aisles. Warehouse capacity for pallets is increased dramatically without losing direct access to each pallet. These systems can be installed to function manually, by remote control or by a computer.
ABOUT US
HIGH DENSITY INC 2022 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED



















